The early steam engine
A few years after opening his instrument shop, another one of Watt's professors brought a steam engine, something still relatively new to the world, to Watt's attention. At this point, Watt had never actually seen an operating, model, but had tried to create one previously that had failed. Watt was frustrated by the failure, and devoted nearly all of his time to learning and understanding the steam engine.
In 1763, Watt discovered that the University of Glasgow had a Newcomen steam engine delivered to them for repairs. Eager to show off his knowledge, Watt jumped on the project of rebuilding the engine.
Watt discovered that the machine had just barley worked because almost 80% of the steam was being consumed in heating the cylinder, due to the steam being condensed by an injected stream of cold water. Watt had the idea of 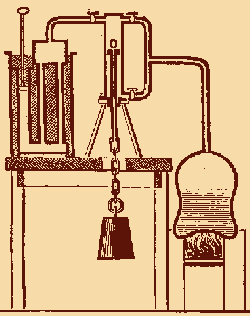 building a chamber that had the steam condense in an area separate from the pistons, which would maintain the pistons at the same temperature of the injected steam. Watt finished his plans in 1765, and had a working model.
building a chamber that had the steam condense in an area separate from the pistons, which would maintain the pistons at the same temperature of the injected steam. Watt finished his plans in 1765, and had a working model.
Now came the real challenge: Building a full scale model ready for use by businesses. This needed a bunch of more money, most of which came from John Roebuck, founder of Carron Ironworks, with who Watt formed a partnership. The main difficulty in their struggles was maintaining the full scale pistons and cylinders. Most of their assets were spent on obtaining a patent, which was hard to do in the United Kingdom at that time. Out of money, Watt was forced to work as a surveyor for eight years, and Roebuck went bankrupt. Eventually Matthew Boulton, who owned the Soho foundry received the patent rights, and him and Watt formed a very successful partnership, which lasted for the next 25 years.
Watt now had the best iron workers in the world, and could get to work. John Wilkinson, a cannon maker, helped Watt design a plan that would work with the larger pistons and cylinders, and in 1776, the first large scale steam engines were operational and in enterprises. The first engines were used as pumps, and Watt received order after order for the next five years for his engine.
